Scientists Detect First Mid-Sized Black Hole via Gravitational Waves

Within just 5 yrs of detecting the first gravitational waves, LIGO and Virgo scientists have but yet again assisted progress our comprehension of the cosmos.
On May well 21, 2019, scientists identified a distinctive established of gravitational waves, or ripples in the cloth of area-time, that they haven’t witnessed before. For a single, the waves came from midway throughout the universe, or about 7 billion gentle-yrs away, creating it the most distant gravitational-wave sign at any time detected.
But extra importantly, the scientists imagine these gravitational waves place to the merger of two by now weird black holes that formed a hardly ever-before-verified mid-sized black hole. In other text, the scientists imagine they’ve uncovered the 1st direct proof for a special breed of black hole known as an intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH).
Astronomers imagine IMBHs fill a hole concerning stellar-mass black holes (which are a several to 100 solar masses and are made when massive stars collapse), and supermassive black holes (which are millions to billions of solar masses and lurk in the facilities of most galaxies). And even though the precise mass variety of each individual class of black hole depends on who you talk to, most astronomers concur that, at 142 solar masses, this newly formed object fits the invoice for an IMBH.
The observations and additional information of the discovery had been printed September 2 in Physical Evaluation Letters, while an investigation of the sign and its implications had been printed the very same working day in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The two progenitor black holes are witnessed spiraling inward before merging in this simulation, developing the gravitational waves detected by LIGO and Virgo. (Credit history: N. Fischer, H. Pfeiffer, A. Buonanno (Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics), Simulating Excessive Spacetimes (SXS) Collaboration)
A Black Gap Desert
The merger sign, known as GW190521, lasted only a tenth of a second — but scientists straight away understood it was amazing in comparison to LIGO’s 1st detection in 2015.
“This does not search a great deal like a ‘chirp,’ which is what we usually detect,” explained Virgo member Nelson Christensen in LIGO’s press release. “This is extra like something that goes ‘bang,’ and it’s the most massive sign LIGO and Virgo have witnessed.”
Unsurprisingly, this peculiar sign was created by the merger of two equally unusual black holes with masses of about 66 and eighty five solar masses, which raises a several issues with regards to their development.
During a usual stellar life time, stars are able to assistance their fat simply because internal fusion create an outward drive that balances the inward crush of gravity. But if a star is massive enough, once it runs out of gas, it can no for a longer time combat gravitational collapse. Ultimately, the main of this kind of a star collapses less than its personal fat before rebounding again out as a dramatic supernova.
But any star that could theoretically kind a black hole concerning sixty five to one hundred twenty solar masses, like possibly progenitor of this distinctive merger, does not explode as supernova. That usually means there should not be any black holes born from collapsing stars in that mass variety.
Rather, when a star that huge starts its dying throes, a phenomenon recognized as “pair instability” kicks in, and the star gets unstable to the place it avoids gravitational collapse — at the very least, for a while. And when it does eventually explode, it leaves almost nothing at the rear of. (On the other end of the spectrum, stars over one hundred twenty solar masses hardly ever go supernova simply because they collapse instantly into black holes.)
“Several situations predict the development of black holes in the so-known as pair instability mass hole: they may possibly end result from the merger of smaller sized black holes,” explained Virgo collaboration member Michela Mapelli in Virgo’s press release. “However, it is also achievable that we have to revise our existing comprehension of the final phases of the star’s everyday living.”
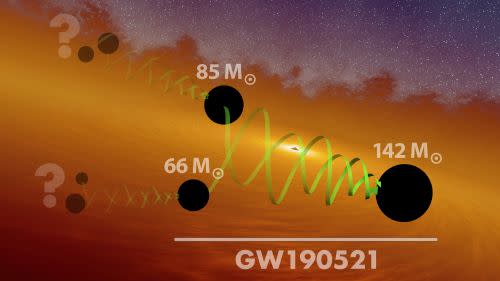
Two main merger events may have formed the progenitor black holes that had been not long ago detected merging to develop an intermediate-mass black hole. (Credit history: LIGO/Caltech/MIT/R. Damage (IPAC))
Stranger Issues
That is not the only unusual component of this gravitational wave occasion, while. The ‘bang’ Christensen mentions was picked up by the extra ‘catch-all’ strategy that LIGO and Virgo use to determine gravitational waves. Alternatively than individuals combing by way of the information, algorithms look for out any indicators that search odd or intriguing.
While unlikely, the scientists admit the signal’s unusually brief length, blended with other unusual elements, suggest GW190521 could have been created by something fully unexpected. But that is element of the exhilaration. “What if something totally new created these gravitational waves?” questioned LIGO collaboration member Vicky Kalogera in a Northwestern press release. “It’s a tantalizing prospect.”
In their paper, the scientists briefly think about what other sorts of resources could be dependable for this 1st-of-its-variety sign. A single likelihood is that the collapse of a star within just our personal Milky Way could have created a equivalent frequency. But scientists imagine that is unlikely simply because other indicators of a neighborhood supernova, this kind of as neutrinos, are lacking. Another likelihood is the sign is the end result of a cosmic string — a hypothetical defect in area-time created in the 1st several times pursuing inflation. Or probably, the two progenitor black holes had been not formed by way of mergers or stellar collapse, but rather started off as primordial black holes.
While these different explanations are inconceivable, they still expose how numerous potential avenues gravitational-wave investigation may unlock. Or, as Virgo spokesperson Giovanni Losurdo explained: “The observations built by Virgo and LIGO are shedding gentle on the darkish universe and defining a new cosmic landscape.”







