Scientists Created Bendable Ice (and It’s Super Cool)
When it arrives to the subject of microfibers, researchers no more time require to “break the ice.” Many thanks to a new discovery in nanomaterials, they can now bend it as an alternative.
“Our team had been working on silica microfibers for twenty decades,” claims Xin Guo, an optical scientist at Zhejiang College in China and one of the authors of a examine printed in Science this summertime. Now, her team has grow to be the 1st to improve microfibers with flexible ice that can bend back upon themselves — without the need of fracturing.
Ice is recognized for remaining a brittle material, largely owing to imperfections in the framework of its crystals. But scientists nonetheless never thoroughly comprehend what‘s happening on a molecular amount when ice changes to h2o and vice versa. The optical homes of the new, ultra-elastic ice microfibers could reveal new insights.
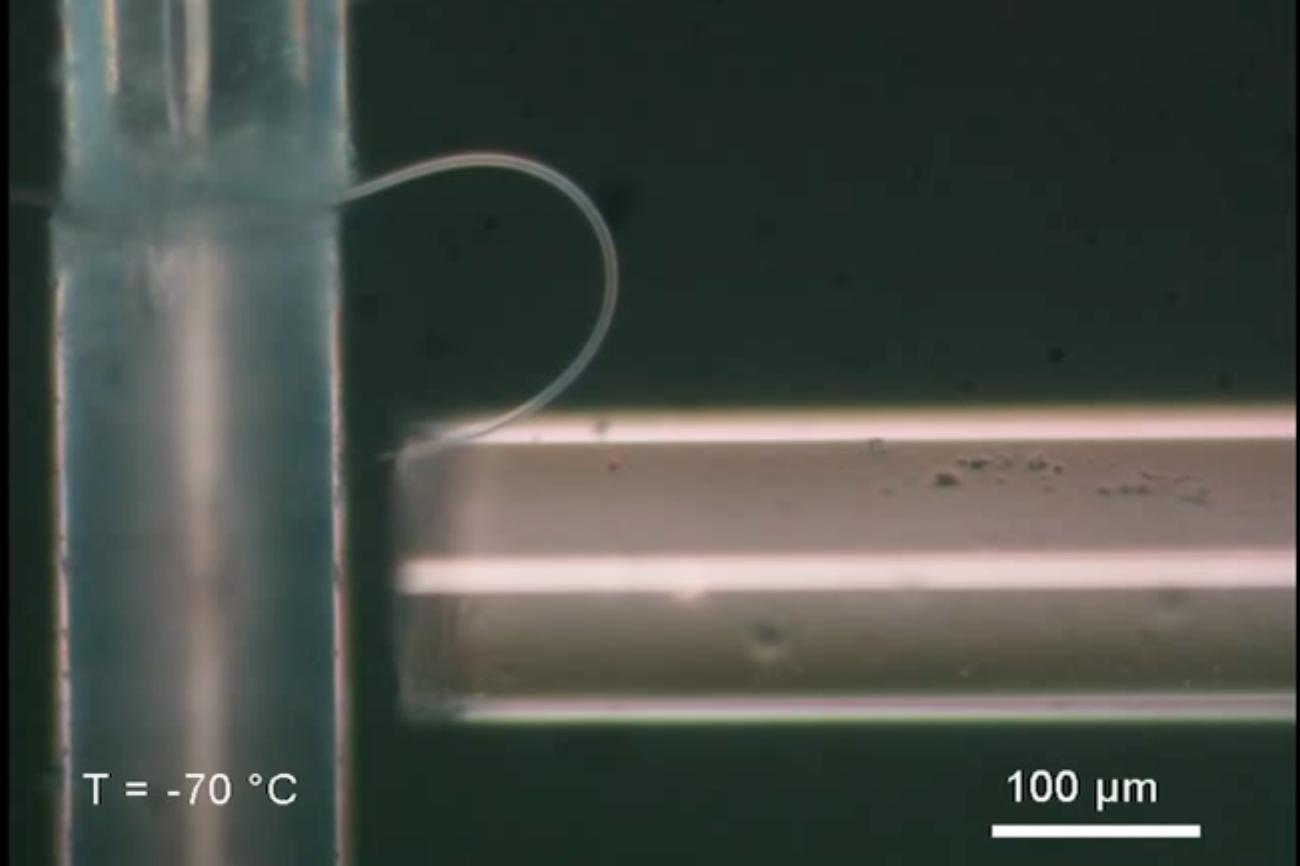
The researchers produced the microfibers by cooling down a tungsten needle (which narrows to the thickness of a solitary atom and is the sharpest item at any time manufactured) in a specific chamber to about –60 degrees Fahrenheit, Guo claims. That is colder than any other former experiment of this character. The team then used an electric powered field to draw h2o vapor to the needle suggestion. As the vapor froze there, it fashioned a microfiber about 5 micrometers in diameter and about one millimeter in duration.
“It’s really slender and really quick,” claims Limin Tong, also an optical scientist at Zhejiang College and a co-creator of the examine. Guo provides that the fiber was fashioned with solitary crystal ice. “We fabricated [a] substantial-high quality ice microfiber with a uniform framework,” she claims.
The researchers then reduced the temperature even much more, to concerning –94 degrees and –238 degrees Fahrenheit. When they tried out to bend it, they discovered their experiment had labored. The ensuing fiber could bend up to a greatest pressure of 10.9 per cent — considerably much more than regular ice and near to the 15 per cent theoretical greatest elasticity of ice, while no one has at any time attained everywhere near to that. It also bounces back to its authentic variety.
“It’s just like some magic,” Tong claims of the preliminary attempt to bend the product. “Normally we never have perfect ice crystals. Now we have a kind of microfiber with a really uniform character.”
When “cool” in and of itself, bendable ice can also be practical. The researchers despatched gentle via the ice microfiber, which is really crystal clear, and discovered that it labored just as properly as the silica fibers typically used to transmit information via gentle. Guo and Tong believe these sorts of fibers may well also uncover use in detecting viruses or other microbes by positioning tiny organisms on the microfibers and guiding gentle via them, we could master much more about the focus, density or forms of microbes that may well be existing.
In the potential, the team will also operate on developing sensors that are appropriate with the flexible ice. Of training course, this fiber melts at around fourteen degrees Fahrenheit — this means it may well not be practical in quite a few circumstances. “That is a really typically used temperature in laboratories,” Tong claims, “and also in some sorts of ice cream.” But researchers in the polar areas, or in house, could make use of them owing to the inherently low temperatures.
Perhaps most importantly, gentle shined via these frozen fibers could help researchers examine what occurs when ice changes phases. Simply because a section change can be brought about merely by bending the microfiber, executing so could reveal much more about how ice crystals variety, why they variety the way they do and what molecules are included.
For now, the next action is to decide if more time ice microfibers can be produced. “We have a whole lot of mysteries that are nonetheless unidentified to us as scientists,” Tong claims.






